Pronouns are words used in place or to replace a noun. Examples include he, she, it, they, you, them, who, us, we, their etc.
Table of Contents
Examples in a sentence;
- She took the boy home after he was injured.
- Whom do you think has a lot of money here?
- It has a long tail.
- He is one of the best students in this class.
- They are going to have a kong vacation.
- You play football so well.
Read Also: 20 Basic & Most Important Literary Devices With Examples
Types Of Pronouns
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative Pronouns are pronouns that point out things and persons.
Examples
- That man is a miser.
- This pen belongs to our teacher.
- Those boys are rude; be careful with them.
- Didn’t you know these toys are ours?
- Go and get that car.
Extra
Singular – Plural
This > These
That > Those
Relative Pronouns
Relative Pronouns are pronouns that conjoin two different parts of a sentence. Examples include; whose, whom, which, that and who.
Examples
‘Whose, whom and who’ are relative pronouns used to refer to people.
Examples
- Whose pen did you take home without permission?
- She the girl whose money got lost yesterday.
- Are you the who was looking for me?
- Whom did you share the gift with?
‘Which’ is also used to refer to creatures and things.
Examples
- Which of these shirts belongs to you?
- You like builds which have got elevators right?
- Kumi like cats which have got nice names.
‘That’ is also used to refer to things, creatures and persons.
Examples
- She is the young girl that killed the beast in the movie.
- Anyone that is good gets the best thing in return.
- The student that comes to school early tomorrow will be rewarded.
Read Also: Argumentative Essay: Education Should Be Free For All
Personal Pronouns
Personal Pronouns are pronouns that refers to one or combination of first person, second person and third person.
Personal pronouns are therefore divided into three. They are; first person, second person and third person.
Whereas;
- First person = refers to the person who’s speaking.
- Second person = refers to the person who’s been spoken to.
- Third person = refers to thing or person that is been spoken about.
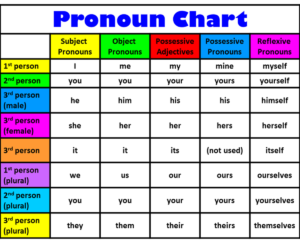
Further, personal pronouns can be used as a subject and an object.
Personal Pronouns Used as ‘Subjects’
Examples
- I am the one who killed the snake.
- You are wiser than your friends.
- We took the ball home.
- It likes to bark even during the day.
- He likes to have tea every night.
- They like to study with their English home teacher.
- She only tackle the problem that’s hard to solve.
Personal Pronouns Used As Objects
- They laughed at me when I failed.
- She hit that ball right at us.
- I’m sure he likes her.
- I saw you taking the wallet home.
- We were flogged for bullying him.
- Are we going to fight them back or what?
- The snake bit her.
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive Pronouns are pronouns that show possession of someone or something.
Examples
- This house is ours.
- The ball is mine.
- These bags are yours.
- That book is his.
- I agree that, the purse is hers.
- Did you know that, the phone was theirs?
Read Also: Brief History Of English Literature – Simplified
Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive Pronouns are pronouns that have the form of ‘self’ or ‘selves’ as a suffix to show that the action delivered by the subject is affected by itself.
Examples
- The cat cleans itself all the time.
- Always remind yourself of who you are.
- Be deceiving yourselves that, the assignment is easy.
- He washes himself in the bathroom.
- They go to the club to cool themselves down.
Note that, reflexive pronouns can also be used to make emphasis. These are also known as Emphatic Pronouns.
Examples
- He drove the car all by himself.
- They fought the authorities all by themselves.
- I washed my parent’s clothes myself.
- It chased the robbers out of the house all by itself.
Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative Pronouns are pronouns that are used in both direct or indirect questions.
Interrogative pronouns can be used for persons, things and other creatures.
‘Who, whom and whose‘ are used for persons
Examples
- Whose car is that?
- Whom did you tell before going out?
- Who took my bag from the wardrobe?
‘What’ is used for things and other creatures.
Examples
- What did you say to her?
- What do you like when I’m coming home?
‘Which’ is also used for persons, things and other creatures.
Examples
- Which of these bags is nice?
- Which do you love most?
Read Also: How To Deal With Emotional Pain
Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal Pronouns are pronouns that can be used to conjoin two different sentences together.
Examples
- Ahmed helped Fauzia.
- Fauzia helped Ahmed.
Therefore: Ahmed and Fauzia helped each other.
- Tony hates the cat.
- The cat also hates Tony.
Therefore: They hate each other.
- Larry loves Franca.
- Franca loves Larry.
Therefore: Franca and Larry love each other.
- All of the boys love one another
- The tennis teams that played on the pitch hate one another.
Extra: ‘One another‘ is used in a sentence when there are more than two subjects in the sentence while ‘each other’ is also used when there are just two subjects in the sentence.
Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite Pronouns are pronouns that are used to refer to things or persons without mentioning them.
Examples
Many, all, most, another, any, anyone, anybody, everyone, everything, anything, everybody, either, neither, oneself, more, most, each, each one, none, nobody, no one, nothing, few, many, least, both, each etc.
Examples in a sentence
- Everyone is invited but you.
- None of these guys are good.
- Nothing surprises me anymore.
- Anyone’s game is good.
- Neither you nor him will enter the stadium today.
- All of your bad deeds are weighed just as your good deeds would be.
- Each one of you is a genius.
- She took several oranges home.
- Some of you deserve to be promoted.
- Most of the players were awesome during the game.
- Everything is going into flame.
- Their teacher likes none of those boys.
Read Also: Bullying In Schools – Stats, Types, Effects, Signs, Solutions
Some Common Problems With The Usage Of Pronouns
1. All pronouns that are used after prepositions must be in the ‘object’ form. Also, you should be very careful if there are two pronouns after the preposition.
Examples
- The girl fell behind me.
- Please don’t talk to him.
- They give everyone the food but us.
- Nancy is the bridge between them.
Two pronouns after preposition
- She slept before you and me.
- Kande insulted them and us.
- Please don’t talk to him and me.
2. After the word ‘Let’ is used in a sentence, always use the ‘Object’ form of the pronoun.
Examples
- Let you and me swim today✔
- Let you and I swim today❌
- Let her take the garbage for us✔
- Let her take the garbage for we❌
- Let your brother feed them✔
- Let your brother feed they❌
3. After using the words ‘as’ and ‘than’, it is right to use the ‘subject’ form of the pronoun.
Examples
- You are as wise as I✔
- You are as wise as me❌
- My mother is richer than she✔
- My mother is richer than her❌
- Kamil is as smart as they✔
- Kamil is as smart as them❌
4. All pronouns that are used before(am, are, is, was, will be, have, has etc) should be in the ‘subject’ form. And all the forms of the verb ‘to be‘.
Examples
- Is seen to be
- Is said to be
- Is believed to be
- Is supposed to be
- Is realised to be
Common Mistakes
- It is he✔ not It is him❌
- It is we✔ not It is us❌
- Its is they✔ not It is them❌
- It is I✔ not It is me✔(note that, ‘it is me’ is also correct)
- It is she✔ not It is her❌
- It is you✔
- It is supposed to be she✔ not It is supposed to be her❌
- The talent coach is said to be he✔ not The talent coach is said to be him❌
- The pundits are seen to be we✔ not The pundits are seen to be us❌
- He is mostly mistaken to be I✔ not He is mostly mistaken to be me❌